The Absorb™ Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold (BVS) is a fully dissolving stent and is now an option. The Absorb dissolving heart stent is the first and only device of its kind – a coronary drug-eluting stent that dissolves completely in the body over time. Absorb treats coronary artery disease by keeping the diseased vessel open to restore blood flow, but then dissolves and disappears after the artery is healed.
Oklahoma Heart Institute was the first hospital to perform the Absorb™ Dissolving Stent in Northeastern Oklahoma.
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
When the arteries supplying blood to your heart become narrowed or blocked by plaque, there is less blood going to the heart muscle and the heart has to work harder. Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, pain in the jaw or radiating to arm, nausea, vomiting, etc. Metal stents have been used as one treatment form for coronary artery disease and the stents remain in the body permanently. This does not allow the vessel to have the exact same motion as it would without the metal stent.
What is the Absorb™ Dissolving Stent?
The Absorb dissolving heart stent is a coronary stent that dissolves completely in the body over time. While stents are traditionally made of metal, Abbott’s Absorb stent is made of a naturally dissolving material, similar to dissolving sutures. Absorb disappears in about 3 years, leaving only two pairs of tiny metallic markers that remain in the artery to enable a physician to see where the device was placed. After it has done its job of keeping a clogged artery open and promoting healing of the treated artery segment it is completely gone; in contrast, metal stents are permanent implants.
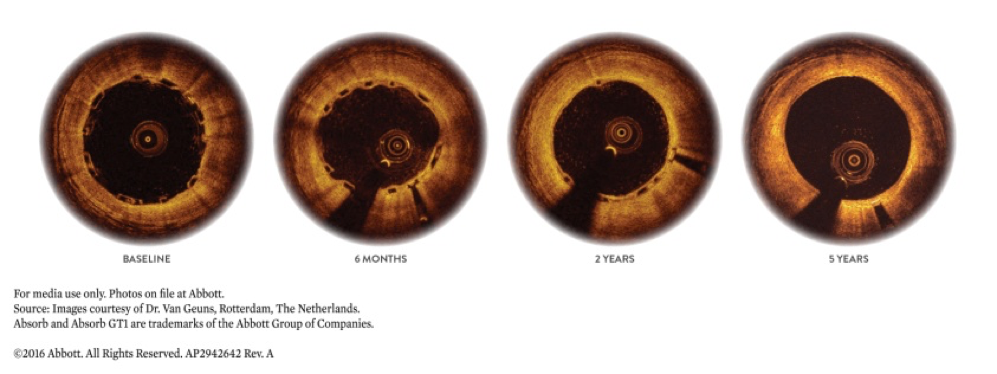
What are the Benefits of Absorb™ Dissolving Stent?
The job of the Absorb™ Dissolving Stent remains the same as the metallic stent – to keep the clogged artery open while the artery heals. But this advance in technology allows the artery to return to a more natural state after the stent dissolves.
- After the stent dissolves, the vessel regains natural motion
- Clinical studies indicate comparable outcomes to metallic stents
